pacman::p_load(tidyverse, jsonlite, SmartEDA, tidygraph, ggraph)In-class Exercise 5
0.1 Installing and Loading the Required Libraries
0.2 Importing Data
kg <- fromJSON("data/MC1_graph.json")0.2.1 Inspect structure
str(kg,max.level = 1)List of 5
$ directed : logi TRUE
$ multigraph: logi TRUE
$ graph :List of 2
$ nodes :'data.frame': 17412 obs. of 10 variables:
$ links :'data.frame': 37857 obs. of 4 variables:0.2.2 Extract and inspect
nodes_tbl <- as_tibble(kg$nodes)
edges_tbl <- as_tibble(kg$links)0.3 Initial EDA
ggplot(data = edges_tbl,
aes(y = `Edge Type`)) +
geom_bar()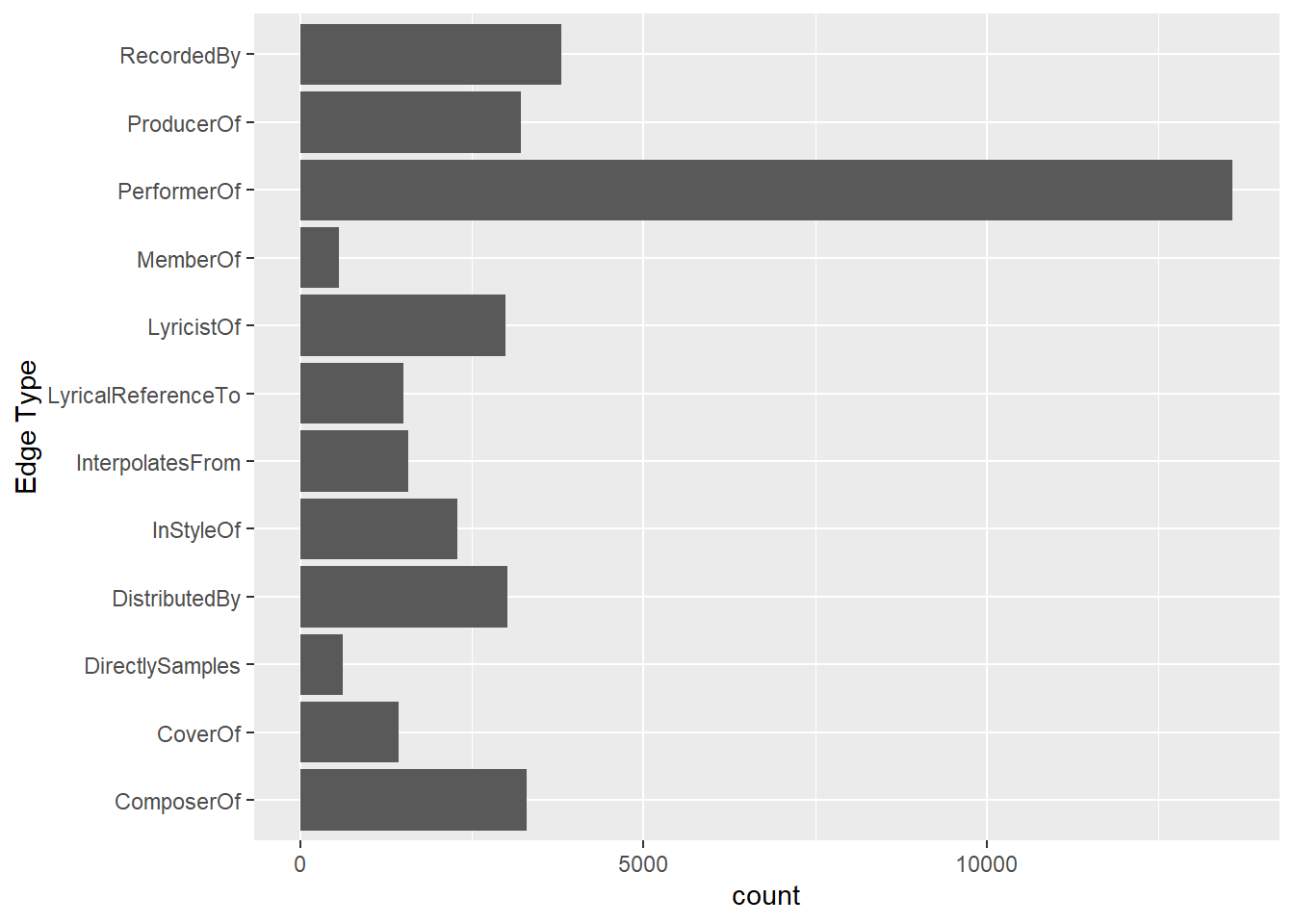
ggplot(data = nodes_tbl,
aes(y = `Node Type`)) +
geom_bar()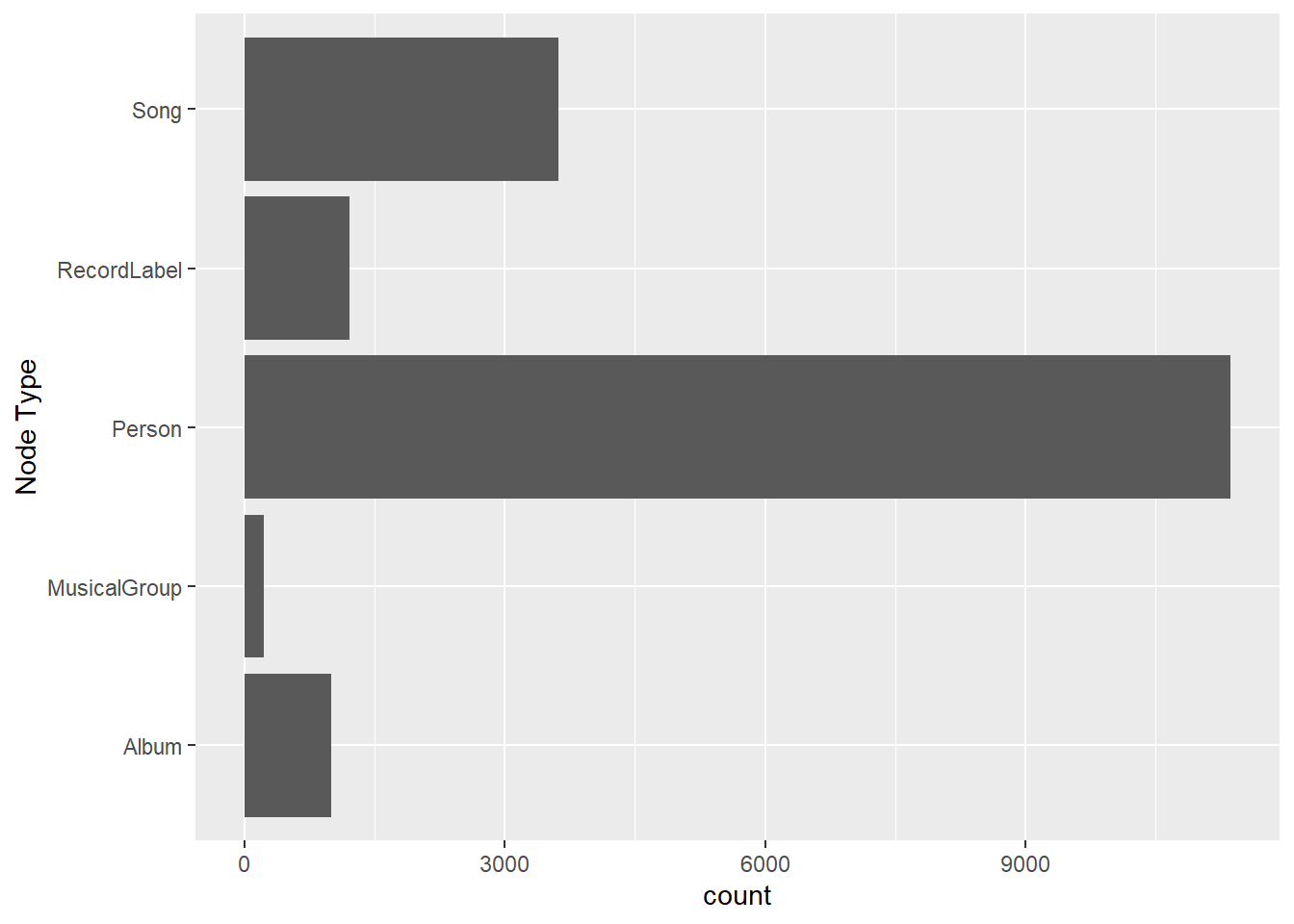
0.4 Creating Knowledge Graph
0.4.1 Step 1: Mapping from node id to row index
id_map <- tibble(id = nodes_tbl$id,
index = seq_len(
nrow(nodes_tbl)))This ensures each id from your node list is mapped the correct row number.
0.4.2 Step 2: Map source and target IDs to row indices
edges_tbl <- edges_tbl %>%
left_join(id_map, by = c("source" = "id")) %>%
rename(from = index) %>%
left_join(id_map, by = c("target" = "id")) %>%
rename(to = index)0.4.3 Step 3: Filter out any unmatched (invalid) edges
edges_tbl <- edges_tbl %>%
filter(!is.na(from), !is.na(to))0.4.4 Step 4: Creating the graph
graph <- tbl_graph(nodes = nodes_tbl,
edges = edges_tbl,
directed = kg$directed)0.5 Visualising the knowledge graph
set.seed(1234)0.6 Visualising the whole graph
ggraph(graph, layout = "fr") +
geom_edge_link(alpha = 0.3,
colour = "gray") +
geom_node_point(aes(colour = "Node Type"),
size = 4) +
geom_node_text(aes(label = name),
repel = TRUE,
size = 2.5) +
theme_void()0.7 Visualising the sub-graph
0.7.1 Step 1: Filter edges to only “MemberOf”
graph_memberof <- graph %>%
activate(edges) %>%
filter(`Edge Type` == "MemberOf")0.7.2 Step 2: Extract only connected nodes (i.e., used in these edges)
used_node_indices <- graph_memberof %>%
activate(edges) %>%
as_tibble() %>%
select(from, to) %>%
unlist() %>%
unique()0.7.3 Step 3: Keep only those nodes
graph_memberof <- graph_memberof %>%
activate(nodes) %>%
mutate(row_id = row_number()) %>%
filter(row_id %in% used_node_indices) %>%
select(-row_id) #optional cleanup0.7.4 Plot the sub-graph
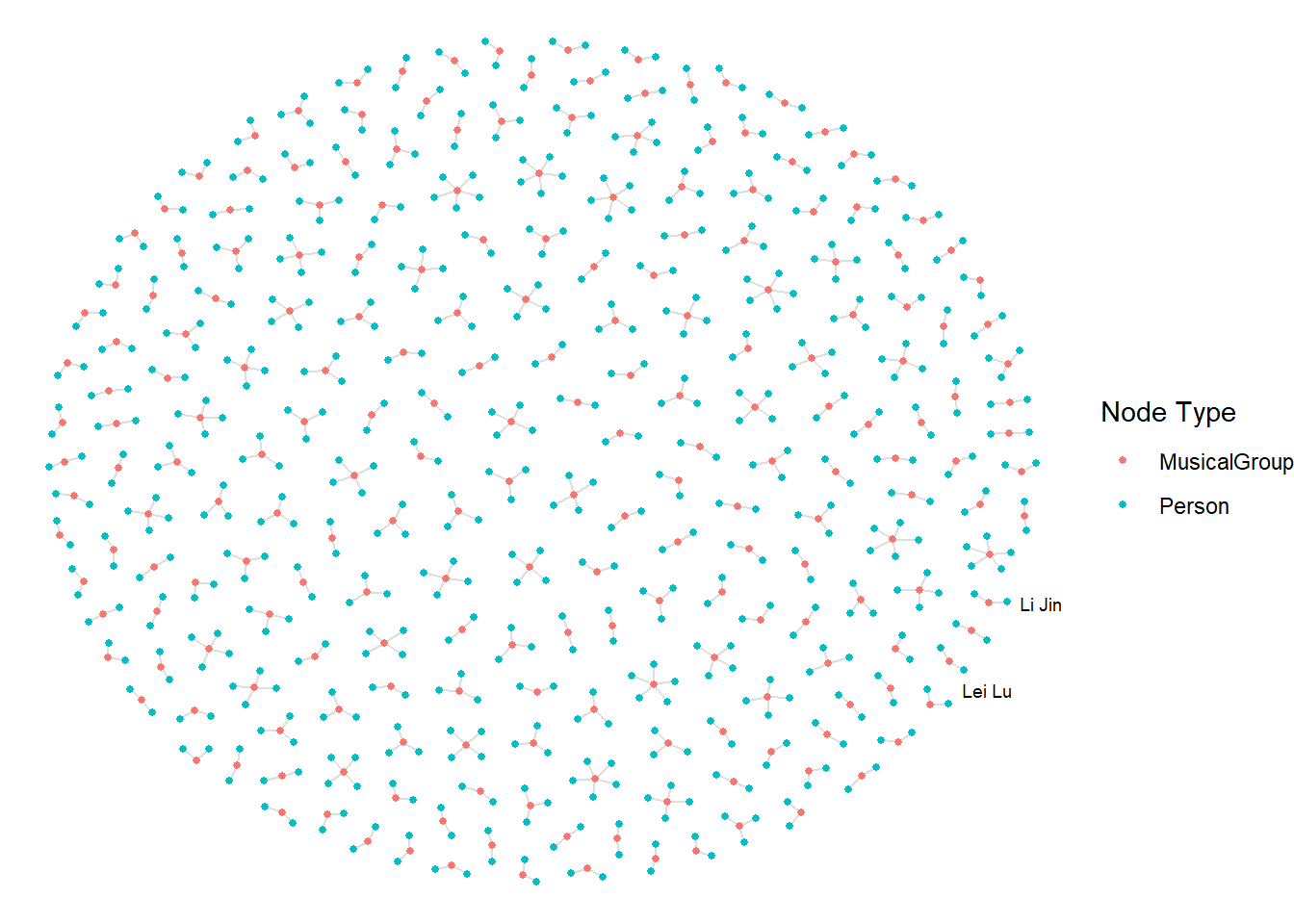
ggraph(graph_memberof,
layout = "fr") +
geom_edge_link(alpha = 0.5,
colour ="gray") +
geom_node_point(aes(colour = `Node Type`),
size = 1) +
geom_node_text(aes(label = name),
repel = TRUE,
size = 2.5) +
theme_void()Warning: ggrepel: 789 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider
increasing max.overlaps